Agate Geode Gemstone Information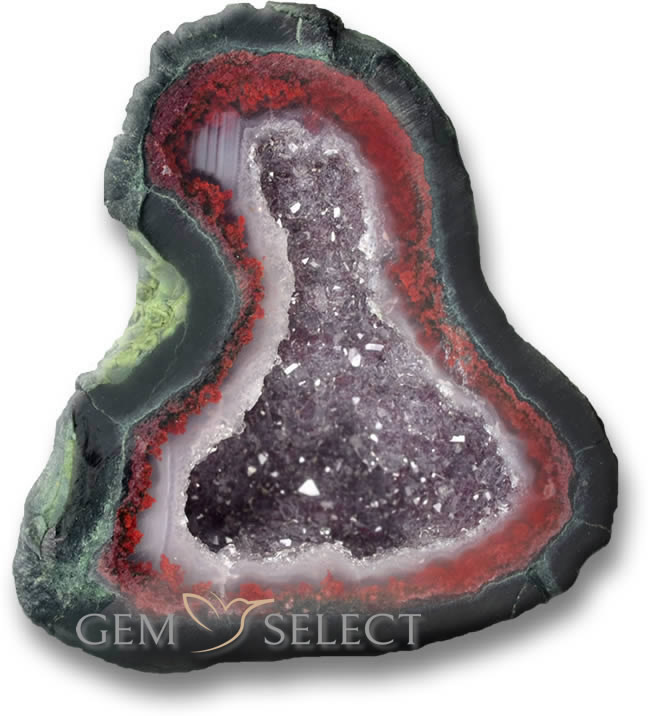 Buy Agate Geode Gemstones from GemSelect
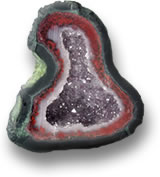
About Agate Geodes – History and IntroductionOn the outside, agate geodes appear to be nothing but rock, but looking deeper into the interior of a geode will reveal amazing crystal growth and formations. Agate geode crystals are usually composed of quartz or chalcedonic deposits, but various other minerals such as calcite, celestite and dolomite are also commonly found within other varieties of geodes. Most geodes develop in small hollow burrows within the earth, often created by animals or depressions left by tree roots. The formation begins from a small piece of limestone or anhydrite and over time, mineral-rich waters seep into the burrow allowing the minerals to harden around the small rock. It is through the repetitive series of hardening deposits from mineral-rich waters that eventually form the crystalline structure and outer crust of the geode.
Identifying geodes requires a great amount of skill. Untrained eyes will struggle to identify geodes because of their plain appearance. Skilled miners focus on the outcrops of rock and look specifically in environments where geodes are most likely to develop. Miners will look for any egg-shaped stones or unusual stones with cauliflower-like formations. Agate Geode Origin and Gemstone SourcesBack to Top The term ‘geode’ originated from a Greek term meaning ‘shape of the earth’. The name was likely given because of their natural, round earth-like formations, although most occur in oblong or egg-like shapes. Geodes can be found all around the world, but they are mostly located in deserts and volcanic regions. Geodes are especially abundant throughout America including California, Illinois, Nevada, Arizona, Missouri, Kentucky, Utah and Iowa. The crystal production that develops within a geode depends on several variables including the amount of moisture trapped within the geode, the various chemicals and rich minerals deposited, and the amount of pressure applied to the geode. If the balance of these variables is just right, crystal formations will begin to grow within the walls of the shell. The crystals build and grow inward towards the center, slowly filling the geode out. The entire process takes millions of years. Many geode specimens have been estimated to be over 250 million years old. Surprisingly, the majority of agate geode specimens are never completely filled out. Geodes with filled out crystal formations are referred to as nodules; nodules composed of agate are referred to as ‘thundereggs’. Geodes can also develop within bubbles of volcanic rock. Minerals get trapped within cavities deposited through steam and with each deposit, the various minerals harden and form around a seed rock, typically limestone. Crystal development will vary based on the rate and duration of moisture deposits. If water was deposited slowly and with very few impurities, the geode crust will be finely lined with crystal, but if moisture deposits were rapidly made, the cavity will develop with bands of quartz, usually as banded agate. Buying Agate Geode and Determining its Gemstone ValueBack to Top
Agate Geodes Gemological Properties:Back to Top
Agate geodes can occur in a wide variety of colors and patterns. Most trade names or varieties are simply names that refer to the locality or region that the geode was formed. Other varieties of geodes are sometimes named after the crystal growth itself. Other popular geodes, include citrine geodes and amethyst geodes. In many cases, geodes are confused with drusy gemstones. Druzy gemstones exhibit tiny crystals, rather than larger crystal growths, that formed within or on the surface of another mineral. Both drusy gemstones and geode gemstones are often cut into flat plates rather than rounded half-egg shaped stones. These types of stones are often referred to as ‘crystal clusters’ or ‘crystal plates’. Most Popular Similar or Related Gemstone Varieties – Trade Names:Amethyst geode, citrine geode, azurite drusy, rainbow pyrite drusy, thunderegg, Bristol diamonds, quartz geode, chalcedony geode, jasper geode, limonite geode and calcite geode are among the most common varieties of geodes and drusys. Lesser Known Similar or Related Gemstone Varieties – Trade Names:Uvarovite garnet drusy, hemimorphite drusy, dolomite geode, celestite geode, pyrite geode, kaolinite geode, sphalerite geode, millerite geode, barite geode coconut geode and smithsonite geode are among the lesser known geode and drusy trade names. Agate Geode Gemstone Mythology, Metaphysical, Alternative HealingBack to Top Agate geodes carry the same healing powers as all other agate crystals. In addition, most geodes contain other minerals, thus carrying the powers of all minerals contained within. Geodes in general are known to have very strong powers. Geodes are believed to be able to help see the ‘whole perspective’ and to see situations from different viewpoints. Agate geodes are also believed to be able to help shape someone’s future. They can bridge communications and they are also helpful for clearing one’s mind for meditation. Agate geodes are especially powerful in alleviating stress and strengthening spirituality.
Agate Geode Gemstone and Jewelry Design IdeasBack to Top Agate geodes are unusual in shape, so most are sliced when used in jewelry designs. Agate geodes are very popular for gemstone jewelry, carvings, cameos, beads and cabochons. Geodes make excellent ornamental gems and are most ideal for pendants, pins, brooches or earrings. Note: Buy colored gemstones by size and not by carat weight. Colored stones vary in size-to-weight ratio. Some stones are larger and others are smaller than diamonds by weight in comparison.
|


 Agate geodes should be cleaned using plain water and mild soap. Using a soft cloth may not be efficient when trying to clean crevices. A soft brush, such as a toothbrush,can be used to clean geodes but care should be taken to ensure not too much pressure is applied. Do not use any harsh chemicals or cleaners to clean geodes and rinse only with room temperature water. Geodes can also be soaked in water to help soften and remove hardened debris.
Agate geodes should be cleaned using plain water and mild soap. Using a soft cloth may not be efficient when trying to clean crevices. A soft brush, such as a toothbrush,can be used to clean geodes but care should be taken to ensure not too much pressure is applied. Do not use any harsh chemicals or cleaners to clean geodes and rinse only with room temperature water. Geodes can also be soaked in water to help soften and remove hardened debris.